Easily deploying Presto on AWS with Terraform
In the past year or so we have been involved in creating several data-lakes and data-warehouses - some from scratch and some in a brownfield environment where we had to either switch from traditional SQL clusters or run side-by-side with them.
Our tool of choice for running SQL on top of "BigData" has been Presto for a while now:
Presto is an open source distributed SQL query engine for running interactive analytic queries against data sources of all sizes ranging from gigabytes to petabytes.
Presto was designed and written from the ground up for interactive analytics and approaches the speed of commercial data warehouses while scaling to the size of organizations like Facebook.
The migration process, with all tools and methods we are using is a topic for many blog-posts, but in this post I wanted to make you aware of our automation around deploying Presto on AWS that we have made available on GitHub.
In the presto-cloud-deploy repository are Packer and Terraform scripts to deploy Presto as a cluster on AWS within 30 minutes or so.
Features:
- Fully functional deployment of Presto in a cluster mode (1 coordinator and multiple workers)
- Spot / Preemptible worker instances supported.
- Single coordinator-worker node deployment mode supported for testing and experimentation.
- Auto-healing features baked in.
- Easily manage and add more catalogs (connect Presto to more data-sources).
- AWS deployment support (under
terraform-aws)
Go get it now from GitHub: https://github.com/BigDataBoutique/presto-cloud-deploy
Presto 101
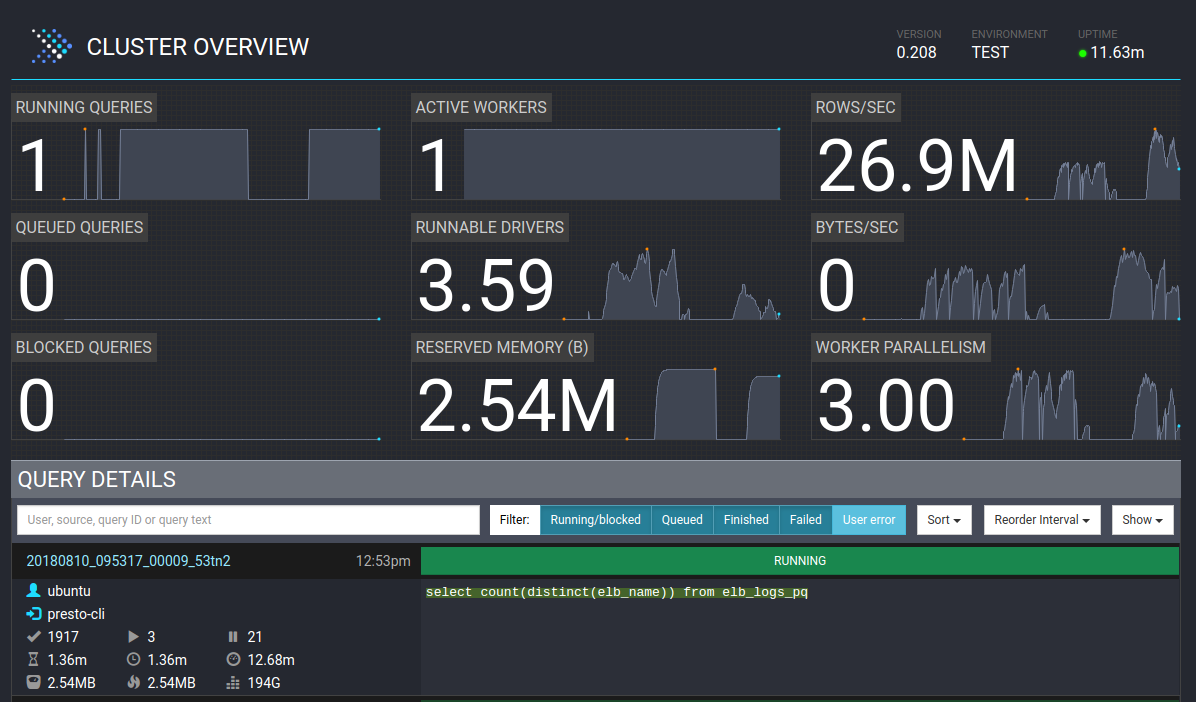
Presto has a nice UI for viewing cluster operations and currently running queries. Once deployed, it can be accessed from http://presto-coordinator-ip:8080/ui/.
In order to run queries, you can connect to Presto via JDBC or SSH into the coordinator node and use the Presto CLI:
presto --catalog hive --schema default
Note the use of Presto's "catalogs". A Catalog in Presto is a definition of a connection to a data-source. A Catalog can be a schema on a MySQL server, an S3 bucket with partitions and schema that is defined in Hive Metastore, data on Kafka or Cassandra, and many other such options. The use of Catalogs makes it possible to query and join data from multiple data-sources in one Presto query.
By default, we enable the local Hive Metastore catalog, and the JMX catalog. To customize or add your own, see the catalogs folder. Changes to this folder require running packer again.
See here for more Presto concepts.
Configuration
Presto needs to be carefully fine-tuned for best performance, mainly taking good care of memory allocations, number of cores and parallelisation (number of concurrent queries, splits, etc). This can only be achieved through experimentation, but at the base of this deployment is a good starting point for a typical cluster. We will be adding more guidance and more configuration options soon.
Try it out
The fastest way to test your installation is to follow AWS Athena's examples in https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/big-data/analyzing-data-in-s3-using-amazon-athena/. If you are running on AWS, this should work out-of-the-box, otherwise you will need to specify your AWS credentials in the hive catalog.
SSH into the Presto coordinator VM and run the Hive REPL ($HIVE_HOME/bin/hive), and within it run the following DDL:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS elb_logs_pq (
request_timestamp string,
elb_name string,
request_ip string,
request_port int,
backend_ip string,
backend_port int,
request_processing_time double,
backend_processing_time double,
client_response_time double,
elb_response_code string,
backend_response_code string,
received_bytes bigint,
sent_bytes bigint,
request_verb string,
url string,
protocol string,
user_agent string,
ssl_cipher string,
ssl_protocol string )
PARTITIONED BY(year int, month int, day int)
STORED AS PARQUET
LOCATION 's3a://athena-examples/elb/parquet/'
tblproperties ("parquet.compress"="SNAPPY");
msck repair table elb_logs_pq;
This will create a partitioned "external" Hive table with data on S3. Once done, you can query it via Hive, or you can logout of Hive and query it via the Presto CLI:
ubuntu@ip-172-31-32-64:~$ presto --catalog hive --schema default
presto:default> SELECT elb_name,
-> sum(case elb_response_code
-> WHEN '200' THEN
-> 1
-> ELSE 0 end) AS uptime, sum(case elb_response_code
-> WHEN '404' THEN
-> 1
-> ELSE 0 end) AS downtime
-> FROM elb_logs_pq
-> GROUP BY elb_name;
elb_name | uptime | downtime
--------------+-----------+----------
elb_demo_004 | 383616619 | 21261503
elb_demo_008 | 383360093 | 21350497
elb_demo_002 | 383632502 | 21300518
elb_demo_009 | 383427076 | 21335844
elb_demo_001 | 383671436 | 21270594
elb_demo_007 | 383490605 | 21303122
elb_demo_005 | 383734702 | 21341740
elb_demo_003 | 383351477 | 21231655
elb_demo_006 | 383506485 | 21336487
(9 rows)
Query 20180810_121913_00002_s3bz8, FINISHED, 3 nodes
Splits: 2,418 total, 2,418 done (100.00%)
0:53 [3.84B rows, 2.51GB] [71.7M rows/s, 48MB/s]
I will be blogging more about Presto and how we build and extend data-lakes with it very soon, but just wanted to put this out there so you can try it out yourself.